We have support for Javascript in both our Integration Apps and Integration Steps. This means you have full control over the data and can do whatever data transformation you want and even make other transactions during the execution of an Action on an App.
We have 4 different scripting options for you:
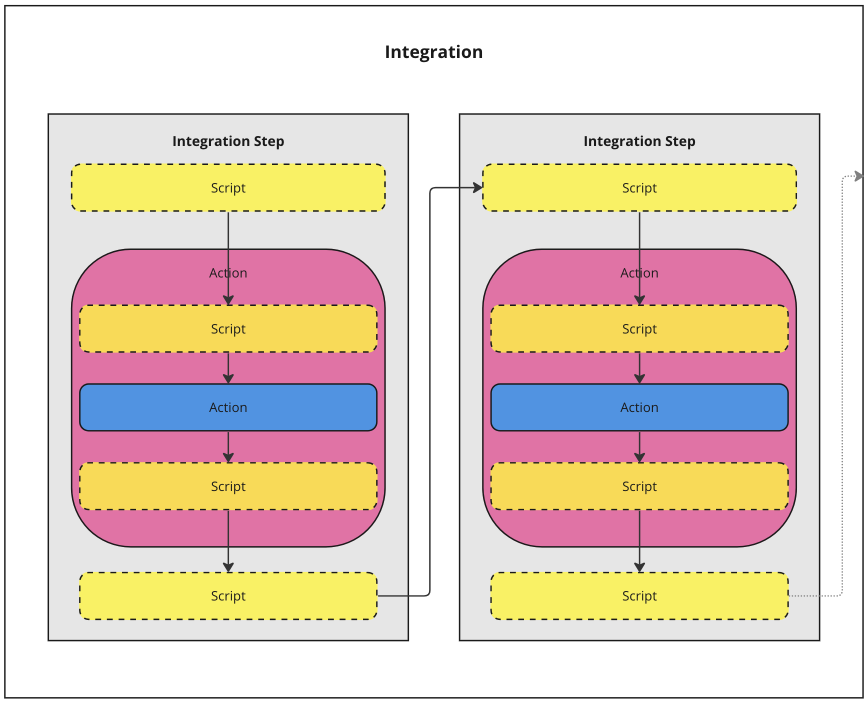
Step in an Integration is executedAction is executed on an AppAction has been executed on an AppStep in an Integration has been executedEach script saves and uses variables from other steps and scripts.

Each integration consists of one or more steps. The first step can have a trigger and one action. The rest of the steps only have actions. Each step executes a script before the action is executed, and after the execution.
Also, before an action is executed, the action’s own start script is executed. After the executed action, another script is executed. The scripts can modify the data that is sent to and from the action, and return a value other steps can use.
Your scripts must contain a main function with one argument and it must return something (or null).
function main(arg) {
return "Hello World!";
}
In Copyl, you can write scripts using a subset of the JavaScript language. Initially based on the ECMAScript 5.1 standard, Copyl now supports many features from ECMAScript 6 (ES6) and later versions, enhancing its scripting capabilities. This allows you to use a wide range of JavaScript features, including:
var, let, and const for variable management, with let and const offering block-scoped declarations.if, for, while, and switch are supported.() => {}).Math, Date, JSON, and more.Hello, ${name}!) for easy string interpolation.try/catch/finally.Despite these enhancements, there are some limitations to be aware of:
window, document, or the DOM.async/awaityieldimport and export)function generateUUID() {
var d = new Date().getTime(); // Current timestamp
return 'xxxxxxxx-xxxx-4xxx-yxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx'.replace(/[xy]/g, function(c) {
var r = (d + Math.random() * 16) % 16 | 0;
d = Math.floor(d / 16);
return (c === 'x' ? r : (r & 0x3 | 0x8)).toString(16);
});
}
Copyl has a lot of specialized functions for file management, integration orchestration and data transformation.
This is a broad feature that we have documented separately. You can use the AI functions together with all other scripting features listed below.
httpGet(url, headersJson): Makes a HTTP GET request to the specified URL. The headersJson should be a JSON string that contains Headers property. Returns the response body as a string.
var getResponse = await httpGet("<https://api.example.com/resource>", "{\\"Headers\\":{\\"Authorization\\":\\"Bearer token\\"}}");httpPost(url, requestBody): Makes a HTTP POST request to the specified URL. The requestBody should be a JSON string that contains Headers and Body properties. Returns the response body as a string.Example: var postResponse = await httpPost("<https://api.example.com/resource>", "{\\"Headers\\":{\\"Content-Type\\":\\"application/json\\",\\"Authorization\\":\\"Bearer token\\"},\\"Body\\":\\"{\\\\\\"key\\\\\\":\\\\\\"value\\\\\\"}\\"}");httpPut(url, requestBody): Makes a HTTP PUT request to the specified URL. The requestBody should be a JSON string that contains Headers and Body properties. Returns the response body as a string.Example: var putResponse = await httpPut("<https://api.example.com/resource>", "{\\"Headers\\":{\\"Content-Type\\":\\"application/json\\",\\"Authorization\\":\\"Bearer token\\"},\\"Body\\":\\"{\\\\\\"key\\\\\\":\\\\\\"value\\\\\\"}\\"}");httpDelete(url, headersJson): Makes a HTTP DELETE request to the specified URL. The headersJson should be a JSON string that contains Headers property. Returns the response body as a string.Example: var deleteResponse = await httpDelete("<https://api.example.com/resource>", "{\\"Headers\\":{\\"Authorization\\":\\"Bearer token\\"}}");httpPatch(url, requestBody): Makes a HTTP PATCH request to the specified URL. The requestBody should be a JSON string that contains Headers and Body properties. Returns the response body as a string.Example: var patchResponse = await httpPatch("<https://api.example.com/resource>", "{\\"Headers\\":{\\"Content-Type\\":\\"application/json\\",\\"Authorization\\":\\"Bearer token\\"},\\"Body\\":\\"{\\\\\\"key\\\\\\":\\\\\\"value\\\\\\"}\\"}");zip(sourceDirectory, destinationFile): Creates a zip file from a directory. Example: zip("/path/to/source", "/path/to/destination.zip")unzip(sourceFile, destinationDirectory): Extracts a zip file to a directory. Example: unzip("/path/to/source.zip", "/path/to/destination")ftpGetFilesAndDirectories(host, username, password, remoteDirectory): This function connects to a FTP server using the provided host, username, and password, and returns a list of files and directories in the specified remote directory. The function is asynchronous and returns a Promise that resolves to an array of strings.Example: var filesAndDirs = await ftpGetFilesAndDirectories('ftp.example.com', 'username', 'password', '/remote/path');ftpUploadFile(host, username, password, localFilePath, remoteFilePath): Uploads a file to an FTP server. The parameters are:
host: The hostname or IP address of the FTP server.username: The username to authenticate with the FTP server.password: The password to authenticate with the FTP server.localFilePath: The path to the local file to upload.remoteFilePath: The path on the FTP server where the file should be uploaded.ftpDownloadFile(host, username, password, remoteFilePath, localFilePath): Downloads a file from an FTP server. The parameters are the same as for ftpUploadFile, but localFilePath and remoteFilePath are swapped.sshGetFilesAndDirectories(host, username, password, remoteDirectory): This function connects to a SFTP server using the provided host, username, and password, and returns a list of files and directories in the specified remote directory. The function is asynchronous and returns a Promise that resolves to an array of strings.Example: var filesAndDirs = await sshGetFilesAndDirectories('sftp.example.com', 'username', 'password', '/remote/path');sshDownloadFile(host, username, password, remoteFilePath, localFilePath): Downloads a file from an SFTP server. The parameters are the same as for ftpDownloadFile.sshUploadFile(host, username, password, localFilePath, remoteFilePath): Uploads a file to an SFTP server. The parameters are the same as for ftpUploadFile.runTrigger(triggerId, integrationAppTriggerEvent, apiKey): This function allows you to trigger an integration event. It takes three parameters:The function returns a promise that resolves to the triggered event. Here’s an example of how to use it:var triggerId = Guid.Parse("your-trigger-id");var integrationAppTriggerEvent = { /* your event data */ };var apiKey = "your-api-key";runTrigger(triggerId, integrationAppTriggerEvent, apiKey).then(function(event) {console.log("Triggered event: ", event);});
triggerId: The ID of the trigger.integrationAppTriggerEvent: An object representing the integration app trigger event. This object should have the same structure as the IntegrationAppTriggerEvent class in your application.apiKey: The API key for authentication.runIntegration(integrationId, enterpriseId): Runs an integration with the specified integration ID and enterprise ID. This function is asynchronous and returns a task that represents the running integration. Example: var result = await runIntegration("12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789012", "12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789012");Note: Replace the example GUIDs with the actual IDs of the integration and enterprise you want to run.addStepData(data, name): Adds data other steps in the integration can use. Example: addStepData("john", "name"); is then available as step1_out_name (please change step number to your step)stopStep(): Stops the current step of the integration. Example: stopStep();stopIntegration(): Stops the current step and the rest of the integration. Example: stopIntegration();newGuid(): Generates a new UUID/GUID.emptyGuid(): Generates an empty UUID/GUID.throwException(message): Throws an exception with the specified message. Example: throwException("This is an error message")getSecretValue(secretName): Returns the unencrypted secret value for the secret with that name. Example: var db = getSecretValue('dbConnectionString');log(message): Logs a message in the integration log. Example: log("This is a log message.");sendEmail(to, from, subject, message): Sends an email. Example: sendEmail("[email protected]", "[email protected]", "Hello", "This is a test email.");base64Encode(input): Encodes a string to Base64. Example: base64Encode("Hello World") returns “SGVsbG8gV29ybGQ=”base64Decode(input): Decodes a Base64 string. Example: base64Decode("SGVsbG8gV29ybGQ=") returns “Hello World”charEncode(input): Encodes a string to URL-safe format. Example: charEncode("Hello World") returns “Hello%20World”charDecode(input): Decodes a URL-safe string. Example: charDecode("Hello%20World") returns “Hello World”searchReplace(input, oldValue, newValue): Replaces all occurrences of a specified string within another string. Example: searchReplace("Hello World", "World", "Copyl") returns “Hello Copyl”formatDate(date, format): Formats a date. Example: var formattedDate = formatDate(new Date(), "MM/dd/yyyy");jsonToXml(json): Converts a JSON string to an XML string. Example: var xml = jsonToXml("{\\"name\\":\\"John\\"}");xmlToJson(xml): Converts an XML string to a JSON string. Example: var json = xmlToJson("<name>John</name>");csvToJson(csv): Converts a CSV string to a JSON string. Example: var json = csvToJson("name,age\\nJohn,30");jsonToCsv(json): Converts a JSON string to a CSV string. Example: var csv = jsonToCsv("[{\\"name\\":\\"John\\",\\"age\\":30}]");cleanString(input): Cleans a string. Example: var cleaned = cleanString(" Hello, World! ");toInt(input): Converts a string to an integer. Example: var number = toInt("123");toDate(input): Converts a string to a date. Example: var date = toDate("2023-07-10");extract(input, pattern): Extracts data from a string using a regular expression. Example: var match = extract("Hello, World!", "\\\\w+");sum(numbers): Calculates the sum of a list of numbers. Example: var total = sum([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);average(numbers): Calculates the average of a list of numbers. Example: var avg = average([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);filter(objects, condition): Filters a list of objects based on a condition. Example: var filtered = filter([{name: "John", age: 30}, {name: "Jane", age: 25}], "obj.age > 25");